Electro-optical shutters technique in q switching
In my earlier articles I have discussed the basics of Q-switching and three of its techniques known as mechanical shutters, rotating reflector method and passive shutters. Toady I will discuss the one more following techniques of Q-switching:
Electro-optical Shutters.
To obtain faster switching, the suitable electro-optical effects of altering the refractive index of a cell by applying an electric field is used. Two such effects are:
i) Pockels effect
ii) Kerr effect
i) Pockels effect.
A crystal cell like potassium dihydrogen phosphate (KDP) is a device which when subjected to an applied DC voltage, becomes birefringent. Birefringent crystal is those crystal which split the light wave into two waves travelling at different velocities that is the crystal offers different refractive indices for different polarized light. One wave is called ordinary wave having refractive index n0 and other is called extraordinary wave having refractive index ne. In Pockels effect, the refractive index of material varies linearly with the applied electric field.
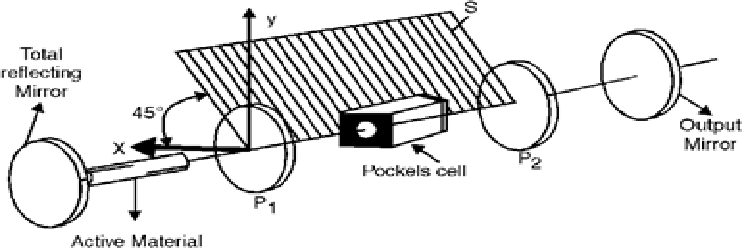
In the laser arrangement designed for Q-switching with a Pockels cell there, in between the active medium and the output reflecting mirror, there are two polarisers (P1 and P2 ) oriented in the same sense that is transmitted light is polarized in the same plane S. The pockels cell is placed between the polarisers P1 and P2.
In the polarizer-Pockels cell-polariser combination, the light travelling to the cell has to pass a polariser P1 and becomes polarised in the S plane. When no voltage is applied to the Pockels cell that is when the cell is OFF, the light traverses the polariser and the cell without any loss except the loss suffered due to absorption.
When voltage is applied to the Pockels cell that is when the cell is ON, then the cell becomes birefringent and rotates the polarisation vector of the light passing through it by 900.
S1 is the new plane of polarisation and is perpendicular to the orientation of polariser P2. Thus, it will not allow the light to pass through output reflecting mirror.
Therefore, when the cell is ON, the passage of light is blocked. In other words, laser cavity Quality factor Q is maximum with the Pockels cell OFF and minimum when the cell is ON.
The switching rate depends on the frequency of the voltage applied to the cell. A Pockel cell requires a small voltage of 1-5 KV. The switching time is about 10-9 sec which is smaller than that with the mechanical shutters. Pulses of 10-8 sec duration with peak power of 106 to 109 watts can be generated with this method.
Above discussion shows that the Pockels cell is used as shutter that is why the name of the process is electro-optical shutter.
ii) Kerr effect.
This effect is different from the Pockel effect in the sense that in Kerr effect the birefringence is proportional to the square of the applied electric field or in other words, in Kerr effect, the refractive index varies as the square of the electric field intensity.
The process of Q-switching is same as discussed in Pockels effect.
Here as the name suggests, Kerr cell is used as electro- optical shutter.
The voltage requires for operation is about 10-20 KV.
Example of the Kerr cell is Nitrobenzene cell.
This is about Electro-optical shutters technique in q switching. I hope you have understood the same.